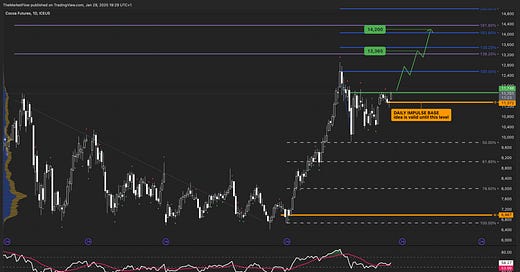
Key Chart (Daily)

The trend is long on the monthly and the weekly, and the market made a 50% correction of the previous impulse.
If the market crosses above the last daily breakdown, it triggers the open of a space for the weekly and the daily target fibo levels as valid targets.
Key Fundamentals
Summary
The global cocoa market is experiencing significant volatility, with prices reaching record highs due to supply constraints and increasing demand. Factors such as adverse weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and structural issues in key producing regions continue to impact the market.
Key Factors
Supply Constraints
Adverse Weather and Disease: Major cocoa-producing countries like Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana have seen a 13% production decline due to the El Niño weather phenomenon and the spread of cocoa swollen shoot virus (CSSV) (Financial Times).
Structural Challenges: Chronic underinvestment in cocoa farms has lowered yields, while many smallholder farmers lack capital to improve productivity (Confectionery News).
Demand Dynamics
Rising Consumption: Global cocoa demand is growing 2-3% annually, driven by emerging markets (Confectionery News).
Market Reactions: Record cocoa prices have caused buyers to delay orders, leading to a 2.7% drop in chocolate sales despite higher revenues for major producers like Barry Callebaut (Financial Times).
Price Trends
Recent Surge: Cocoa futures prices ended December 2024 at record highs, with contracts reaching $11,441 per tonne in London and $11,545 per tonne in New York (International Cocoa Organization).
Future Outlook: Analysts expect prices to remain high in 2025, with cocoa stabilizing around $6,000 per tonne once supply normalizes (Confectionery News).
Actionable Insights
Bullish Case:
Supply deficits caused by adverse weather, disease, and farm underinvestment could sustain high cocoa prices.
Continued global demand growth, particularly from emerging markets, is expected to keep prices elevated.
Bearish Case:
Production recovery due to better weather conditions and farm investments could ease supply shortages and lower prices.
Prolonged high prices may reduce demand or push chocolate manufacturers toward cheaper substitutes.